下面的Java代码,演示了三种常用的Memcached常用驱动的连接方式,所有驱动现在都托管在GitHub上面,大家可以自行查找。
Tag Archives: Java
Java实现CORBA静态绑定(七)
本文主要内容涉及:
- CORBA基本架构
- IDL文件编写
- POA示例实现
- POA+TIE示例实现
- ImplBase示例实现
- ImplBase+TIE示例实现
- Persistent示例实现
HiPersistent.idl
module HiCorba
{
interface HiPersistent
{
string sayHiTo(in string someone);
long add(in long numa, in long numb);
oneway void shutdown();
};
};
JDK提供了工具,可以直接生成stubs及skeletons接口代码:
idlj -fall HiPersistent.idl
编写server端代码:
import java.util.Properties;
import org.omg.CORBA.Object;
import org.omg.CORBA.ORB;
import org.omg.CosNaming.NameComponent;
import org.omg.CosNaming.NamingContextExt;
import org.omg.CosNaming.NamingContextExtHelper;
import org.omg.CORBA.Policy;
import org.omg.PortableServer.POA;
import org.omg.PortableServer.*;
import org.omg.PortableServer.Servant;
import HiCorba.*;
class HiPersistentImpl extends HiPersistentPOA {
private ORB orb;
public void setORB(ORB orb_val) {
orb = orb_val;
}
// implement sayHiTo() method
public String sayHiTo(String someone) {
return "\nHi, "+someone+" !"+"\n";
}
// implement add() method
public int add(int numa, int numb) {
return numa+numb;
}
// implement shutdown() method
public void shutdown() {
orb.shutdown(false);
}
}
public class HiPersistentServer {
public static void main( String args[] ) {
try {
// Step 1: Instantiate the ORB
ORB orb = ORB.init(args, null);
// Step 2: Instantiate the servant
HiPersistentImpl impl = new HiPersistentImpl();
impl.setORB(orb);
// Step 3 : Create a POA with Persistent Policy
// Step 3-1: Get the rootPOA
POA rootPOA = POAHelper.narrow(orb.resolve_initial_references("RootPOA"));
// Step 3-2: Create the Persistent Policy
Policy[] persistentPolicy = new Policy[1];
persistentPolicy[0] = rootPOA.create_lifespan_policy(LifespanPolicyValue.PERSISTENT);
// Step 3-3: Create a POA by passing the Persistent Policy
POA persistentPOA = rootPOA.create_POA("childPOA", null, persistentPolicy );
// Step 3-4: Activate HiPersistentPOA's POAManager, Without this
// All calls to HiPersistent Server will hang because POAManager
// will be in the 'HOLD' state.
persistentPOA.the_POAManager().activate( );
// Step 4: Associate the servant with HiPersistentPOA
persistentPOA.activate_object( impl );
// Step 5: Resolve RootNaming context and bind a name for the
// servant.
// NOTE: If the Server is persistent in nature then using Persistent
// Name Service is a good choice. Even if ORBD is restarted the Name
// Bindings will be intact. To use Persistent Name Service use
// 'NameService' as the key for resolve_initial_references() when
// ORBD is running.
org.omg.CORBA.Object obj = orb.resolve_initial_references( "NameService" );
NamingContextExt rootContext = NamingContextExtHelper.narrow( obj );
NameComponent[] nc = rootContext.to_name( "HiPersistent" );
rootContext.rebind( nc, persistentPOA.servant_to_reference( impl ) );
// Step 6: We are ready to receive client requests
orb.run();
} catch ( Exception e ) {
System.err.println( "Exception in Persistent Server Startup " + e );
}
}
}
编写client端代码:
import java.util.Properties;
import org.omg.CORBA.ORB;
import org.omg.CORBA.OBJ_ADAPTER;
import org.omg.CosNaming.NamingContext;
import org.omg.CosNaming.NamingContextHelper;
import org.omg.CosNaming.NameComponent;
import org.omg.PortableServer.POA;
import HiCorba.*;
public class HiPersistentClient {
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
// Step 1: Instantiate the ORB
ORB orb = ORB.init(args, null);
// Step 2: Resolve the PersistentHelloServant by using INS's
// corbaname url. The URL locates the NameService running on
// localhost and listening on 1900 and resolve
// 'PersistentServerTutorial' from that NameService
org.omg.CORBA.Object obj = orb.string_to_object("corbaname::localhost:1900#HiPersistent");
HiPersistent hiPersistent = HiPersistentHelper.narrow( obj );
// Step 3: Call the sayHello() method every 60 seconds and shutdown
// the server. Next call from the client will restart the server,
// because it is persistent in nature.
while( true ) {
System.out.println( "Calling HiPersisten Server.." );
System.out.println("Message From HiPersisten Server: " + hiPersistent.sayHiTo("neohope") );
System.out.println("70 + 80 = " + hiPersistent.add(70, 80) );
System.out.println( "Shutting down HiPersistent Server.." );
hiPersistent.shutdown( );
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
} catch ( Exception e ) {
System.err.println( "Exception in HiPersistentClient.java..." + e );
e.printStackTrace( );
}
}
}
编译代码:
javac *.java HiCorba/*.java
测试,在三个shell或cmd窗口中依次运行:
#shell01 orbd -ORBInitialPort 1900 -serverPollingTime 200
#shell02 servertool -ORBInitialPort 1900 >>欢迎使用 Java IDL 服务器工具 >>请在提示处输入命令 > register -server HiPersistentServer -applicationName s1 -classpath .
#shell03 java HiPersistentClient >>Calling HiPersisten Server.. >>Message From HiPersisten Server: >>Hi, neohope ! >>70 + 80 = 150 >>Shutting down HiPersistent Server.. >> >>Calling HiPersisten Server.. >>Message From HiPersisten Server: >>Hi, neohope ! >>70 + 80 = 150 >>Shutting down HiPersistent Server..
Java实现CORBA静态绑定(六)
本文主要内容涉及:
- CORBA基本架构
- IDL文件编写
- POA示例实现
- POA+TIE示例实现
- ImplBase示例实现
- ImplBase+TIE示例实现
- Persistent示例实现
ImplBase主要是为了兼容旧代码所提供的,正常情况下,大家是不需要使用的。
JDK提供了工具,可以直接生成stubs及skeletons接口代码:
idlj -fall -oldImplBase Hi.idl idlj -fallTie -oldImplBase Hi.idl
编写server端代码:
import HiCorba.*;
import org.omg.CosNaming.*;
import org.omg.CosNaming.NamingContextPackage.*;
import org.omg.CORBA.*;
import java.util.Properties;
class HiImpl extends _HiImplBase{
private ORB orb;
public void setORB(ORB orb_val){
orb = orb_val;
}
// implement sayHiTo() method
public String sayHiTo(String someone) {
return "\nHi, "+someone+" !"+"\n";
}
// implement add() method
public int add(int numa, int numb) {
return numa+numb;
}
// implement shutdown() method
public void shutdown() {
orb.shutdown(false);
}
}
public class HiServer {
public static void main(String args[]) {
try{
// create and initialize the ORB
ORB orb = ORB.init(args, null);
// create servant and register it with the ORB
HiImpl hiImpl = new HiImpl();
hiImpl.setORB(orb);
// create a tie, with servant being the delegate.
Hi_Tie tie = new Hi_Tie(hiImpl);
// obtain the objectRef for the tie
// this step also implicitly activates the object
Hi href = HiHelper.narrow(tie);
// get the root naming context
org.omg.CORBA.Object objRef = orb.resolve_initial_references("NameService");
NamingContext ncRef = NamingContextHelper.narrow(objRef);
// bind the Object Reference in Naming
NameComponent nc = new NameComponent("Hi", "");
NameComponent path[] = {nc};
ncRef.rebind(path, href);
System.out.println("HiServer ready and waiting ...");
// wait for invocations from clients
orb.run();
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("ERROR: " + e);
e.printStackTrace(System.out);
}
System.out.println("HiServer Exiting ...");
}
}
编写client端代码:
import HiCorba.*;
import org.omg.CosNaming.*;
import org.omg.CosNaming.NamingContextPackage.*;
import org.omg.CORBA.*;
public class HiClient{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
// create and initialize the ORB
ORB orb = ORB.init(args, null);
// get the root naming context
org.omg.CORBA.Object objRef = orb.resolve_initial_references("NameService");
NamingContext ncRef = NamingContextHelper.narrow(objRef);
// resolve the Object Reference in Naming
NameComponent nc = new NameComponent("Hi", "");
NameComponent path[] = {nc};
Hi hiImpl = HiHelper.narrow(ncRef.resolve(path));
System.out.println("Obtained a handle on server object: " + hiImpl);
System.out.println(hiImpl.sayHiTo("neohope"));
System.out.println(hiImpl.add(70, 80));
hiImpl.shutdown();
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("ERROR : " + e) ;
e.printStackTrace(System.out);
}
}
}
编译代码:
javac *.java HiCorba/*.java
测试,在三个shell或cmd窗口中依次运行:
#shell01 orbd -ORBInitialPort 1900
#shell02 java HiServer -ORBInitialPort 1900 >>HiServer ready and waiting ... >>HiServer Exiting ...
#shell03 java HiClient -ORBInitialPort 1900 -ORBInitialHost localhost >>Obtained a handle on server object: IOR:000000000000001349444c3a4869436f7262612f 48693a312e30000000000001000000000000006e000102000000000d3139322e3136382e35362e31 00007dfd00000019afabcb000000000276c739500000000800000001000000001400000000000002 00000001000000200000000000010001000000020501000100010020000101090000000100010100 00000026000000020002 >>Hi, neohope ! >>150
Java实现CORBA静态绑定(五)
本文主要内容涉及:
- CORBA基本架构
- IDL文件编写
- POA示例实现
- POA+TIE示例实现
- ImplBase示例实现
- ImplBase+TIE示例实现
- Persistent示例实现
ImplBase主要是为了兼容旧代码所提供的,正常情况下,大家是不需要使用的。
JDK提供了工具,可以直接生成stubs及skeletons接口代码:
idlj -fall -oldImplBase Hi.idl
编写server端代码:
import HiCorba.*;
import org.omg.CosNaming.*;
import org.omg.CosNaming.NamingContextPackage.*;
import org.omg.CORBA.*;
import java.util.Properties;
class HiImpl extends _HiImplBase{
private ORB orb;
public void setORB(ORB orb_val){
orb = orb_val;
}
// implement sayHiTo() method
public String sayHiTo(String someone) {
return "\nHi, "+someone+" !"+"\n";
}
// implement add() method
public int add(int numa, int numb) {
return numa+numb;
}
// implement shutdown() method
public void shutdown() {
orb.shutdown(false);
}
}
public class HiServer {
public static void main(String args[]) {
try{
// create and initialize the ORB
ORB orb = ORB.init(args, null);
// create servant and register it with the ORB
HiImpl hiImpl = new HiImpl();
hiImpl.setORB(orb);
// get the root naming context
org.omg.CORBA.Object objRef = orb.resolve_initial_references("NameService");
NamingContext ncRef = NamingContextHelper.narrow(objRef);
Hi href = HiHelper.narrow(hiImpl);
// bind the Object Reference in Naming
NameComponent nc = new NameComponent("Hi", "");
NameComponent path[] = {nc};
ncRef.rebind(path, href);
System.out.println("HiServer ready and waiting ...");
// wait for invocations from clients
orb.run();
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("ERROR: " + e);
e.printStackTrace(System.out);
}
System.out.println("HiServer Exiting ...");
}
}
编写client端代码:
import HiCorba.*;
import org.omg.CosNaming.*;
import org.omg.CosNaming.NamingContextPackage.*;
import org.omg.CORBA.*;
public class HiClient{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
// create and initialize the ORB
ORB orb = ORB.init(args, null);
// get the root naming context
org.omg.CORBA.Object objRef = orb.resolve_initial_references("NameService");
NamingContext ncRef = NamingContextHelper.narrow(objRef);
// resolve the Object Reference in Naming
NameComponent nc = new NameComponent("Hi", "");
NameComponent path[] = {nc};
Hi hiImpl = HiHelper.narrow(ncRef.resolve(path));
System.out.println("Obtained a handle on server object: " + hiImpl);
System.out.println(hiImpl.sayHiTo("neohope"));
System.out.println(hiImpl.add(70, 80));
hiImpl.shutdown();
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("ERROR : " + e) ;
e.printStackTrace(System.out);
}
}
}
编译代码:
javac *.java HiCorba/*.java
测试,在三个shell或cmd窗口中依次运行:
#shell01 orbd -ORBInitialPort 1900
#shell02 java HiServer -ORBInitialPort 1900 >>HiServer ready and waiting ... >>HiServer Exiting ...
#shell03 java HiClient -ORBInitialPort 1900 -ORBInitialHost localhost >>Obtained a handle on server object: IOR:000000000000001349444c3a4869436f7262612f 48693a312e30000000000001000000000000006e000102000000000d3139322e3136382e35362e31 000074c300000019afabcb0000000002768712000000000800000001000000001400000000000002 00000001000000200000000000010001000000020501000100010020000101090000000100010100 00000026000000020002 >>Hi, neohope ! >>150
Java实现CORBA静态绑定(四)
本文主要内容涉及:
- CORBA基本架构
- IDL文件编写
- POA示例实现
- POA+TIE示例实现
- ImplBase示例实现
- ImplBase+TIE示例实现
- Persistent示例实现
与POA方式相比,POA-Tie将继承方式,调整为委托方式,降低了软件的耦合度。
JDK提供了工具,可以直接生成stubs及skeletons接口代码:
idlj -fall Hi.idl idlj -fallTie Hi.idl
编写server端代码:
import HiCorba.*;
import org.omg.CosNaming.*;
import org.omg.CosNaming.NamingContextPackage.*;
import org.omg.CORBA.*;
import org.omg.PortableServer.*;
import org.omg.PortableServer.POA;
import java.util.Properties;
class HiImpl extends HiPOA {
private ORB orb;
public void setORB(ORB orb_val) {
orb = orb_val;
}
// implement sayHiTo() method
public String sayHiTo(String someone) {
return "\nHi, "+someone+" !"+"\n";
}
// implement add() method
public int add(int numa, int numb) {
return numa+numb;
}
// implement shutdown() method
public void shutdown() {
orb.shutdown(false);
}
}
public class HiServer{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
// create and initialize the ORB
ORB orb = ORB.init(args, null);
// Get reference to rootpoa & activate the POAManager
POA rootpoa = POAHelper.narrow(orb.resolve_initial_references("RootPOA"));
rootpoa.the_POAManager().activate();
// create servant and register it with the ORB
HiImpl hiImpl = new HiImpl();
hiImpl.setORB(orb);
// create a tie, with servant being the delegate.
HiPOATie tie = new HiPOATie(hiImpl, rootpoa);
// obtain the objectRef for the tie
// this step also implicitly activates the object
Hi href = tie._this(orb);
// get the root naming context
org.omg.CORBA.Object objRef = orb.resolve_initial_references("NameService");
// Use NamingContextExt which is part of the Interoperable
// Naming Service specification.
NamingContextExt ncRef = NamingContextExtHelper.narrow(objRef);
// bind the Object Reference in Naming
String name = "Hi";
NameComponent path[] = ncRef.to_name( name );
ncRef.rebind(path, href);
System.out.println("HiServer ready and waiting ...");
// wait for invocations from clients
orb.run();
}
catch (Exception e){
System.err.println("ERROR: " + e);
e.printStackTrace(System.out);
}
System.out.println("HiServer Exiting ...");
}
}
编写client端代码:
import HiCorba.*;
import org.omg.CosNaming.*;
import org.omg.CosNaming.NamingContextPackage.*;
import org.omg.CORBA.*;
public class HiClient{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
// create and initialize the ORB
ORB orb = ORB.init(args, null);
// get the root naming context
org.omg.CORBA.Object objRef = orb.resolve_initial_references("NameService");
// Use NamingContextExt instead of NamingContext. This is
// part of the Interoperable naming Service.
NamingContextExt ncRef = NamingContextExtHelper.narrow(objRef);
// resolve the Object Reference in Naming
String name = "Hi";
Hi hiImpl = HiHelper.narrow(ncRef.resolve_str(name));
System.out.println("Obtained a handle on server object: " + hiImpl);
System.out.println(hiImpl.sayHiTo("neohope"));
System.out.println(hiImpl.add(70, 80));
hiImpl.shutdown();
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("ERROR : " + e) ;
e.printStackTrace(System.out);
}
}
}
编译代码:
javac *.java HiCorba/*.java
测试,在三个shell或cmd窗口中依次运行:
#shell01 orbd -ORBInitialPort 1900
#shell02 java HiServer -ORBInitialPort 1900 >>HiServer ready and waiting ... >>HiServer Exiting ...
#shell03 java HiClient -ORBInitialPort 1900 -ORBInitialHost localhost >>Obtained a handle on server object: IOR:000000000000001349444c3a4869436f7262612f 48693a312e300000000000010000000000000086000102000000000d3139322e3136382e35362e31 0000744700000031afabcb00000000207673791300000001000000000000000100000008526f6f74 504f4100000000080000000100000000140000000000000200000001000000200000000000010001 00000002050100010001002000010109000000010001010000000026000000020002 >>Hi, neohope ! >>150
Java实现CORBA静态绑定(三)
本文主要内容涉及:
- CORBA基本架构
- IDL文件编写
- POA示例实现
- POA+TIE示例实现
- ImplBase示例实现
- ImplBase+TIE示例实现
- Persistent示例实现
POA(Portable Object Adapter)提供了一组服务器端的接口以及操作,包括:跟踪侍服对象的实例化以及内存空间信息、服务对象的激活以及反激活、对象引用的创建、对象生命周期的管理等。
JDK提供了工具,可以直接生成stubs及skeletons接口代码:
idlj -fall Hi.idl
编写server端代码:
import HiCorba.*;
import org.omg.CosNaming.*;
import org.omg.CosNaming.NamingContextPackage.*;
import org.omg.CORBA.*;
import org.omg.PortableServer.*;
import org.omg.PortableServer.POA;
import java.util.Properties;
class HiImpl extends HiPOA {
private ORB orb;
public void setORB(ORB orb_val) {
orb = orb_val;
}
// implement sayHiTo() method
public String sayHiTo(String someone) {
return "\nHi, "+someone+" !"+"\n";
}
// implement add() method
public int add(int numa, int numb) {
return numa+numb;
}
// implement shutdown() method
public void shutdown() {
orb.shutdown(false);
}
}
public class HiServer {
public static void main(String args[]) {
try{
// create and initialize the ORB
ORB orb = ORB.init(args, null);
// get reference to rootpoa & activate the POAManager
POA rootpoa = POAHelper.narrow(orb.resolve_initial_references("RootPOA"));
rootpoa.the_POAManager().activate();
// create servant and register it with the ORB
HiImpl hiImpl = new HiImpl();
hiImpl.setORB(orb);
// get object reference from the servant
org.omg.CORBA.Object ref = rootpoa.servant_to_reference(hiImpl);
Hi href = HiHelper.narrow(ref);
// get the root naming context
// NameService invokes the name service
org.omg.CORBA.Object objRef = orb.resolve_initial_references("NameService");
// Use NamingContextExt which is part of the Interoperable
// Naming Service (INS) specification.
NamingContextExt ncRef = NamingContextExtHelper.narrow(objRef);
// bind the Object Reference in Naming
String name = "Hi";
NameComponent path[] = ncRef.to_name( name );
ncRef.rebind(path, href);
System.out.println("HiServer ready and waiting ...");
// wait for invocations from clients
orb.run();
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("ERROR: " + e);
e.printStackTrace(System.out);
}
System.out.println("HiServer Exiting ...");
}
}
编写client端代码:
import HiCorba.*;
import org.omg.CosNaming.*;
import org.omg.CosNaming.NamingContextPackage.*;
import org.omg.CORBA.*;
public class HiClient
{
static Hi hiImpl;
public static void main(String args[])
{
try{
// create and initialize the ORB
ORB orb = ORB.init(args, null);
// get the root naming context
org.omg.CORBA.Object objRef = orb.resolve_initial_references("NameService");
// Use NamingContextExt instead of NamingContext. This is
// part of the Interoperable naming Service.
NamingContextExt ncRef = NamingContextExtHelper.narrow(objRef);
// resolve the Object Reference in Naming
String name = "Hi";
hiImpl = HiHelper.narrow(ncRef.resolve_str(name));
System.out.println("Obtained a handle on server object: " + hiImpl);
System.out.println(hiImpl.sayHiTo("neohope"));
System.out.println(hiImpl.add(70, 80));
hiImpl.shutdown();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("ERROR : " + e) ;
e.printStackTrace(System.out);
}
}
}
编译代码:
javac *.java HiCorba/*.java
测试,在三个shell或cmd窗口中依次运行:
#shell01 orbd -ORBInitialPort 1900
#shell02 java HiServer -ORBInitialPort 1900 >>HiServer ready and waiting ... >>HiServer Exiting ...
#shell03 java HiClient -ORBInitialPort 1900 -ORBInitialHost localhost >>Obtained a handle on server object: IOR:000000000000001349444c3a4869436f7262612f 48693a312e300000000000010000000000000086000102000000000d3139322e3136382e35362e31 0000732000000031afabcb000000002076625c7400000001000000000000000100000008526f6f74 504f4100000000080000000100000000140000000000000200000001000000200000000000010001 00000002050100010001002000010109000000010001010000000026000000020002 >>Hi, neohope ! >>150
Java实现CORBA静态绑定(二)
本文主要内容涉及:
- CORBA基本架构
- IDL文件编写
- POA示例实现
- POA+TIE示例实现
- ImplBase示例实现
- ImplBase+TIE示例实现
- Persistent示例实现
要写一个静态绑定的CORBA程序,首先要完成的就是定义接口。CORBA采用的接口描述方式为IDL(Interface Description Language),IDL的语法规则类似于CPP,所以Java的类型需要做类型映射。常见类型映射关系如下:
| IDL Type | Java Type |
| module | package |
| boolean | boolean |
| char, wchar | char |
| octet | byte |
| string, wstring | java.lang.String |
| short, unsigned short | short |
| long, unsigned long | int |
| long long, unsigned long long | long |
| float | float |
| double | double |
| fixed | java.math.BigDecimal |
| enum, struct, union | class |
| sequence, array | array |
| interface (non-abstract) | signature interface and an operations interface, helper class, holder class |
| interface (abstract) | signature interface, helper class, holder class |
| constant (not within an interface) | public interface |
| constant (within an interface) | fields in the Java signature interface for non-abstract, or the sole Java interface for abstract |
| exception | class |
| Any | org.omg.CORBA.Any |
| type declarations nested within interfaces | “scoped” package |
| typedef | helper classes |
| pseudo objects | pseudo interface |
| readonly attribute | accessor method |
| readwrite attribute | accessor and modifer methods |
| operation | method |
现在,写一个很简单的IDL文件:
hi.idl
module HiCorba
{
interface Hi
{
string sayHiTo(in string someone);
long add(in long numa, in long numb);
oneway void shutdown();
};
};
Java实现CORBA静态绑定(一)
本文主要内容涉及:
- CORBA基本架构
- IDL文件编写
- POA示例实现
- POA+TIE示例实现
- ImplBase示例实现
- ImplBase+TIE示例实现
- Persistent示例实现
CORBA(Common Object Request Broker Architecture),即公用对象请求代理程序体系结构,是一种为解决分布式处理环境中硬件和软件系统的互连而提出的一种解决方案。其基本架构如下:
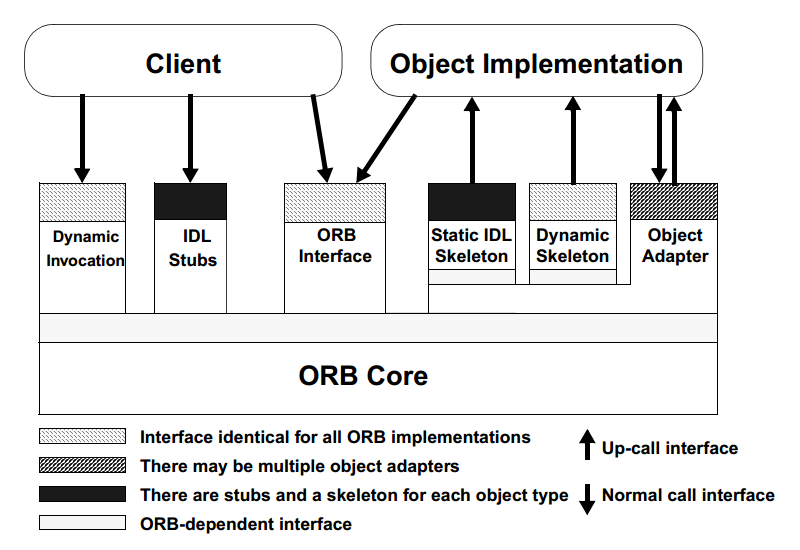
Object Services,即对象服务,是为使用和实现对象而提供的基本对象集合,这些服务应独立于应用领域。主要的CORBA服务有:名录服务(Naming Service)、事件服务(Event Service)、生命周期服务(Life Cycle Service)、关系服务(Relationship Service)以及事务服务(Transaction Service)等。这些服务几乎包括分布系统和面向对象系统的各个方面,每个组成部分都非常复杂。
IDL(Interface Description Language),即接口定义语言,是用来描述软件组件接口的一种规范语言。用户可以定义模块、接口、属性、方法、输入输出参数,甚至异常等等。IDL在不同的语言下都有相应的实现,可以把IDL描述的接口编译为目标语言,包括客户端代理和服务器端框架,以及相应的帮助类等等。比如Java中提供过了idlj命令用来编译。
ORB(Object Request Broker),即对象请求代理,是一个中间件,在对象间建立客户-服务器的关系。通过 ORB,一个客户可以很简单地使用服务器对象的方法而不论服务器是在同一机器上还是通过一个网络访问。ORB 截获调用然后负责找到一个对象实现这个请求,传递参数和方法,最后返回结果。客户不用知道对象在哪里,是什么语言实现的,他的操作系统以及其他和对象接口无关的东西。
CORBA按接口绑定方式,分为两大类,一类为动态绑定,一类为静态绑定。这里主要讲的是静态绑定。
在静态绑定时,客户端需要实现IDL Stubs,服务端需要实现IDL Skeleton。
在静态绑定中,CORBA在服务端实现IDL接口有两种方式,一种为继承模式(分为标准模式POA及兼容模式ImplBase),另一种为为委托模式(分为标准模式POA/Tie及兼容模式ImplBase/Tie)。各模式的区别主要在于生成IDL代码时,输入的参数不同,从而生成的接口不同,实现方式也略有区别。这里主要讲的为标准模式。
一次典型的CORBA调用,流程如下图所示:
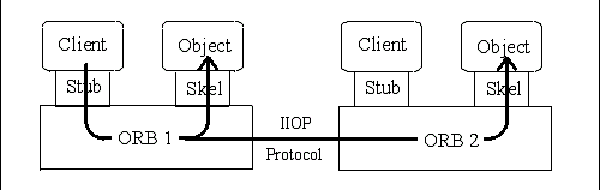
GIOP(General Inter-ORB Protocol),即通用对象请求代理间通信协,提供了一个标准传输语法(低层数据表示方法)和ORB之间通信的信息格式集。GIOP只能用在ORB与ORB之间,而且,只能在符合理想条件的面向连接传输协议中使用。它不需要使用更高一层的RPC机制。这个协议是简单的(尽可能简单,但不是简单化),可升级的,使用方便。它被设计为可移动的、高效能的表现、较少依靠其它的低层传输协议。当然,由于不同传输使用不同版本的GIOP,它们可能不能直接协作工作,但它能很容易的连接网络域。
IIOP (Internet Inter-ORB Protocol),即Internet对象代理间通信协议,指出如何通过TCP/IP连接交换GIOP信息。IIOP为Internet提供了一个标准的协作工作协议,它使兼容的ORB能基于现在流行的协议和产品进行“out of the box”方式的协作工作。它也能被用于两个半桥(half-bridges )之间的协议。该协议能用于任何ORB与IP(Internet Protocol)域之间的协作工作,除非ORB选择了特殊的协议。这时,它是TCP/IP环境下基本的inter-ORB 协议,最普遍的传输层。
GIOP 不基于任何特别的网络协议,OMG 在最广泛使用的通信传输平台 — TCP/IP 上标准化 GIOP,GIOP 加 TCP/IP 等于 IIOP。
NIO多端口监听
1、NIOServerTest.java
package com.neohope.multisocket;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class NIOServerTest {
public static void StartSockets() throws IOException {
Selector selector = Selector.open();
int[] ports = {4000, 4001, 4002};
for (int port : ports) {
ServerSocketChannel server = ServerSocketChannel.open();
server.configureBlocking(false);
server.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
//只处理了建立连接的消息
server.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
}
int serverPort = 0;
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = null;
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = null;
SocketChannel clientChannel = null;
while (selector.isOpen()) {
selector.select();
Set<SelectionKey> readyKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = readyKeys.iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey selectedKey = keyIterator.next();
keyIterator.remove();
if (selectedKey.isAcceptable()) {
serverChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) selectedKey.channel();
serverPort = serverChannel.socket().getLocalPort();
clientChannel = serverChannel.accept();
clientChannel.configureBlocking(false);
switch (serverPort) {
case 4000:
byteBuffer=ByteBuffer.wrap("welcome to port 4000".getBytes(Charset.forName("UTF-8")));
clientChannel.write(byteBuffer);
break;
case 4001:
byteBuffer=ByteBuffer.wrap("welcome to port 4001".getBytes(Charset.forName("UTF-8")));
clientChannel.write(byteBuffer);
break;
case 4002:
byteBuffer=ByteBuffer.wrap("welcome to port 4002".getBytes(Charset.forName("UTF-8")));
clientChannel.write(byteBuffer);
break;
}
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
StartSockets();
}
}
2、NIOClientTest.java
package com.neohope.multisocket;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.SocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class NIOClientTest {
public static void StartClient(String host, int port)
{
int readSize = 0;
SocketChannel clientChannel = null;
SocketAddress socketAddress = new InetSocketAddress(host, port);
byte[] bytes;
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
try {
clientChannel = SocketChannel.open();
clientChannel.connect(socketAddress);
try {
while ((readSize = clientChannel.read(byteBuffer)) >= 0) {
byteBuffer.flip();
bytes = new byte[readSize];
byteBuffer.get(bytes);
byteArrayOutputStream.write(bytes);
byteBuffer.clear();
//服务端没有主动关闭连接,读取少于1024,假设读取完毕
if(readSize<1024)break;
}
System.out.println(byteArrayOutputStream.toString());
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
byteArrayOutputStream.close();
} catch(Exception ex) {}
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
clientChannel.close();
} catch(Exception ex) {}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
StartClient("localhost",4000);
StartClient("localhost",4001);
StartClient("localhost",4002);
}
}
MongoDB副本集(Java)
还是蛮简单的,驱动把任务全部做掉了
package com.djhu.mongodb.test;
import java.util.Arrays;
import org.bson.Document;
import com.mongodb.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.ServerAddress;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
public class ReplTest
{
private static void testInsert()
{
MongoClient mongoClient = new MongoClient(Arrays.asList(
new ServerAddress("172.16.172.4", 27017),
new ServerAddress("172.16.172.4", 27018),
new ServerAddress("172.16.172.4", 27019)));
MongoDatabase db = mongoClient.getDatabase("test");
MongoCollection collection = db.getCollection("person");
Document doc = new Document();
doc.put("name", "tuzi");
doc.put("age", 27);
doc.put("sex", "Female");
collection.insertOne(doc);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
testInsert();
}
}
如果遇到下面的错误,是因为用了localhost作为replSet的地址,重新config一下就好了
Caused by: java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused: connect
at java.net.PlainSocketImpl.socketConnect(Native Method)
at java.net.PlainSocketImpl.doConnect(PlainSocketImpl.java:333)
at java.net.PlainSocketImpl.connectToAddress(PlainSocketImpl.java:195)
at java.net.PlainSocketImpl.connect(PlainSocketImpl.java:182)
at java.net.SocksSocketImpl.connect(SocksSocketImpl.java:366)
at java.net.Socket.connect(Socket.java:519)
at com.mongodb.connection.SocketStreamHelper.initialize(SocketStreamHelper.java:50)
at com.mongodb.connection.SocketStream.open(SocketStream.java:58)
... 3 more
Exception in thread "main" com.mongodb.MongoTimeoutException: Timed out after 30000 ms while waiting for a server that matches PrimaryServerSelector. Client view of cluster state is {type=REPLICA_SET, servers=[{address=localhost:27017, type=UNKNOWN, state=CONNECTING, exception={com.mongodb.MongoSocketOpenException: Exception opening socket}, caused by {java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused: connect}}, {address=localhost:27018, type=UNKNOWN, state=CONNECTING, exception={com.mongodb.MongoSocketOpenException: Exception opening socket}, caused by {java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused: connect}}, {address=localhost:27019, type=UNKNOWN, state=CONNECTING, exception={com.mongodb.MongoSocketOpenException: Exception opening socket}, caused by {java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused: connect}}, {address=localhost:27020, type=UNKNOWN, state=CONNECTING, exception={com.mongodb.MongoSocketOpenException: Exception opening socket}, caused by {java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused: connect}}]
at com.mongodb.connection.BaseCluster.createTimeoutException(BaseCluster.java:370)
at com.mongodb.connection.BaseCluster.selectServer(BaseCluster.java:101)
at com.mongodb.binding.ClusterBinding$ClusterBindingConnectionSource.<init>(ClusterBinding.java:75)
at com.mongodb.binding.ClusterBinding$ClusterBindingConnectionSource.<init>(ClusterBinding.java:71)
at com.mongodb.binding.ClusterBinding.getWriteConnectionSource(ClusterBinding.java:68)
at com.mongodb.operation.OperationHelper.withConnection(OperationHelper.java:175)
at com.mongodb.operation.MixedBulkWriteOperation.execute(MixedBulkWriteOperation.java:141)
at com.mongodb.operation.MixedBulkWriteOperation.execute(MixedBulkWriteOperation.java:72)
at com.mongodb.Mongo.execute(Mongo.java:747)
at com.mongodb.Mongo$2.execute(Mongo.java:730)
at com.mongodb.MongoCollectionImpl.executeSingleWriteRequest(MongoCollectionImpl.java:482)
at com.mongodb.MongoCollectionImpl.insertOne(MongoCollectionImpl.java:277)
at com.djhu.mongodb.test.ReplTest.testInsert(ReplTest.java:28)
at com.djhu.mongodb.test.ReplTest.main(ReplTest.java:33)